What is an SSL Certificate ?
SSL Certificates are small data files that digitally bind a cryptographic key to an organization’s details. When installed on a web server, it activates the padlock and the https protocol and allows secure connections from a web server to a browser. Typically, SSL is used to secure credit card transactions, data transfer, and logins, and more recently is becoming the norm when securing browsing of social media sites.
SSL Certificates bind together:
- A domain name, server name or hostname.
- An organizational identity (i.e. company name) and location.

Purpose of SSL Certificate
An organization needs to install the SSL Certificate onto its web server to initiate a secure session with browsers. Once a secure connection is established, all web traffic between the web server and the web browser will be secure.
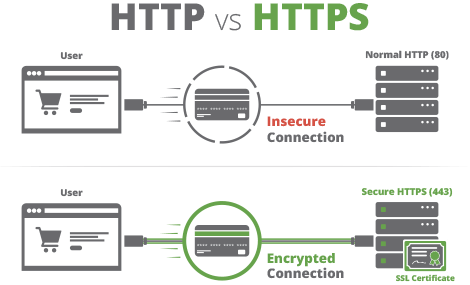
When a certificate is successfully installed on your server, the application protocol (also known as HTTP) will change to HTTPs, where the ‘S’ stands for ‘secure’. Depending on the type of certificate you purchase and what browser you are surfing the internet on, a browser will show a padlock or green bar in the browser when you visit a website that has an SSL Certificate installed.
When a certificate is successfully installed on your server, the application protocol (also known as HTTP) will change to HTTPs, where the ‘S’ stands for ‘secure’. Depending on the type of certificate you purchase and what browser you are surfing the internet on, a browser will show a padlock or green bar in the browser when you visit a website that has an SSL Certificate installed.
How Does an SSL Certificate Work?
SSL CERTIFICATES USE SOMETHING CALLED PUBLIC KEY CRYPTOGRAPHY.
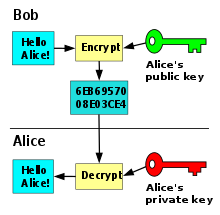
This particular kind of cryptography harnesses the power of two keys which are long strings of randomly generated numbers. One is called a private key and one is called a public key. A public key is known to your server and available in the public domain. It can be used to encrypt any message. If Alice is sending a message to Bob she will lock it with Bob’s public key but the only way it can be decrypted is to unlock it with Bob’s private key. Bob is the only one who has his private key so Bob is the only one who can use this to unlock Alice’s message. If a hacker intercepts the message before Bob unlocks it, all they will get is a cryptographic code that they cannot break, even with the power of a computer.
If we look at this in terms of a website, the communication is happening between a website and a server. Your website and server are Alice and Bob.
Why Do I Need An SSL Certificate?
SSL Certificates protect your sensitive information such as credit card information, usernames, passwords, etc. It also:
SSL Certificates bind together:
- A domain name, server name or hostname.
- An organizational identity (i.e. company name) and location.
WHAT IS AN SSL CERTIFICATE AND HOW DOES IT WORK?
One of the most important components of online business is creating a trusted environment where potential customers feel confident in making purchases. SSL certificates create a foundation of trust by establishing a secure connection. To ensure visitors their connection is secure, browsers provide visual cues, such as a lock icon or a green bar.
SSL certificates have a key pair: a public and a private key. These keys work together to establish an encrypted connection. The certificate also contains what is called the “subject,” which is the identity of the certificate/website owner.
To get a certificate, you must create a Certificate Signing Request (CSR) on your server. This process creates a private key and public key on your server. The CSR data file that you send to the SSL Certificate issuer (called a Certificate Authority or CA) contains the public key. The CA uses the CSR data file to create a data structure to match your private key without compromising the key itself. The CA never sees the private key.
Once you receive the SSL certificate, you install it on your server. You also install an intermediate certificate that establishes the credibility of your SSL Certificate by tying it to your CA’s root certificate. The instructions for installing and testing your certificate will be different depending on your server.
In the image below, you can see what is called the certificate chain. It connects your server certificate to your CA’s (in this case DigiCert’s) root certification through an intermediate certificate.

How Does the SSL Certificate Create a Secure Connection?
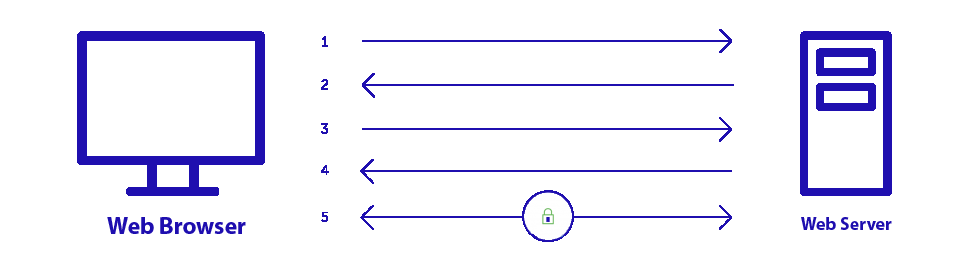
When a browser attempts to access a website that is secured by SSL, the browser and the web server establish an SSL connection using a process called an “SSL Handshake” (see diagram below). Note that the SSL Handshake is invisible to the user and happens instantaneously.
Essentially, three keys are used to set up the SSL connection: the public, private, and session keys. Anything encrypted with the public key can only be decrypted with the private key, and vice versa.
Because encrypting and decrypting with private and public keys takes a lot of processing power, they are only used during the SSL Handshake to create a symmetric session key. After the secure connection is made, the session key is used to encrypt all transmitted data.
SSL certificates have a key pair: a public and a private key. These keys work together to establish an encrypted connection. The certificate also contains what is called the “subject,” which is the identity of the certificate/website owner.
To get a certificate, you must create a Certificate Signing Request (CSR) on your server. This process creates a private key and public key on your server. The CSR data file that you send to the SSL Certificate issuer (called a Certificate Authority or CA) contains the public key. The CA uses the CSR data file to create a data structure to match your private key without compromising the key itself. The CA never sees the private key.
Once you receive the SSL certificate, you install it on your server. You also install an intermediate certificate that establishes the credibility of your SSL Certificate by tying it to your CA’s root certificate. The instructions for installing and testing your certificate will be different depending on your server.
In the image below, you can see what is called the certificate chain. It connects your server certificate to your CA’s (in this case DigiCert’s) root certification through an intermediate certificate.
ENCRYPTION, AUTHENTICATION, TRUST.
Ewebcreative is an authorized reseller of leading certificate authorities and offers a wide-range of SSLs at low cost which is specially designed for individuals and enterprises to establish a secure environment in the age of the cyber world. Our core business is SSL that provides maximum security to the website, extended authentication to manage the business reputation, and boost trust to encourage the customers with HTTPS.
Ewebcreative is a global SSL provider and offers trusted SSL certificates at the cheapest price. We better understand customers’ requirements and maximize our efforts to make their website secure and trustworthy. We have vast experience in the SSL industry and offer cheap SSL certificates to beat the competition. So why should you wait to buy or renew an SSL certificate? Just browse Ewebcreative and get a single solution with robust encryption to secure your entire business.
Essentially, three keys are used to set up the SSL connection: the public, private, and session keys. Anything encrypted with the public key can only be decrypted with the private key, and vice versa.
Because encrypting and decrypting with private and public keys takes a lot of processing power, they are only used during the SSL Handshake to create a symmetric session key. After the secure connection is made, the session key is used to encrypt all transmitted data.
SSL certificates have a key pair: a public and a private key. These keys work together to establish an encrypted connection. The certificate also contains what is called the “subject,” which is the identity of the certificate/website owner.
To get a certificate, you must create a Certificate Signing Request (CSR) on your server. This process creates a private key and public key on your server. The CSR data file that you send to the SSL Certificate issuer (called a Certificate Authority or CA) contains the public key. The CA uses the CSR data file to create a data structure to match your private key without compromising the key itself. The CA never sees the private key.
Once you receive the SSL certificate, you install it on your server. You also install an intermediate certificate that establishes the credibility of your SSL Certificate by tying it to your CA’s root certificate. The instructions for installing and testing your certificate will be different depending on your server.
In the image below, you can see what is called the certificate chain. It connects your server certificate to your CA’s (in this case DigiCert’s) root certification through an intermediate certificate.
